Introduction
Why study VR for soft skills training?
At PwC, digital upscaling is a key part of our journey to foster a digital mindset and enhance the way we work. PwC continually assess new learning technologies and methods to determine how to train employees more efficiently, intelligently, and cost-effectively. The Emerging Technology Group at PwC has been evaluating the business value of Virtual Reality (VR) for several years, particularly in training. VR headsets offer compelling use cases beyond traditional applications like flight simulators, safety procedures, and equipment maintenance training.
Industries such as oil and gas are already experiencing significant improvements in process efficiency through VR-based safety and maintenance simulations. However, we are now exploring whether VR can be equally effective for training in leadership, soft skills, and other human-to-human interactions. Does VR offer advantages over traditional classroom or e-learning methods in these areas? Could VR for business training revolutionise how we develop these crucial skills?

V-learning will likely be an accelerator that helps drive a new age of enterprise training and education by delivering a costeffective, immersive, and efficient experience to train employees on soft skills.
V-learn, which leverages virtual reality to train employees across various skills, has proven more effective than traditional classroom and e-learning methods, particularly in teaching soft skills. V-learners demonstrated up to a 275% increase in confidence to apply what they learned, marking a 40% improvement over classroom training and a 35% improvement over e-learning. Additionally, v-learners were up to four times more focused than their e-learning counterparts. On average, they completed training four times faster than classroom learners and 1.5 times faster than e-learners. Moreover, v-learners were 3.75 times more emotionally engaged with the content compared to classroom learners and 2.3 times more connected than those using e-learning. Beyond these advantages, V-learn also proved to be more cost-effective than classroom or e-learning when implemented at scale.
These findings indicate that VR is ready for deployment on an enterprise scale. A small team successfully provisioned, deployed, and managed a large fleet of VR headsets (head-mounted displays, or HMDs). While VR training may not entirely replace classroom or e-learning methods in the near future, it should be integrated into a blended learning curriculum for specific skill sets. Combining classroom, e-learn, and v-learn offers employees a leading-edge approach to training. V-learning is poised to be a powerful catalyst, ushering in a new era of enterprise training by providing a cost-effective, immersive, and efficient method for developing soft skills.

Measurement
By late 2018, PwC had already trained over 13,000 leaders in inclusive leadership. With V-learn training set to launch in August 2019, we needed to recruit enough leaders to participate in our study. Annually, more than 700 senior associates are promoted to manager at PwC. We identified that by including these associates, along with new senior experienced hires and leaders who had missed both the classroom and e-learn courses, the total number of potential study participants could exceed 1,600.
We carefully selected our test group and divided them into three categories, with each group participating in one of the following training sessions: classroom, e-learn, or v-learn using VR headsets. This study not only provided insights into the effectiveness of VR for business training but also highlighted the potential applications of VR in the oil and gas industry, where immersive learning can significantly enhance skill development and safety protocols.

We also conducted experience surveys and carried out face-to-face and phone interviews to gather insights into the learner experience. Throughout the development of the v-learn course, the team engaged with test user groups to refine the course's effectiveness and assess their sentiments regarding the virtual reality experience. Based on the feedback from UX testers, we made iterative improvements to the course throughout the summer. These findings significantly contributed to our understanding of the population's readiness for VR-based learning.
Employees trained using VR completed training faster
PwC was able to train employees up to four times faster using VR headsets compared to traditional classroom methods and 1.5 times faster than e-learning. Initially, we were surprised to see digital natives struggle with the VR headsets, but once they became accustomed to the technology, most found it user-friendly. Even when factoring in the additional onboarding time for new users—averaging an extra 10 minutes—VR training still proved to be three times faster than classroom training and 1.15 times faster than e-learning. This demonstrates the efficiency of VR for business training and highlights its potential benefits in industries such as oil and gas, where immersive training can enhance skill development and operational safety.
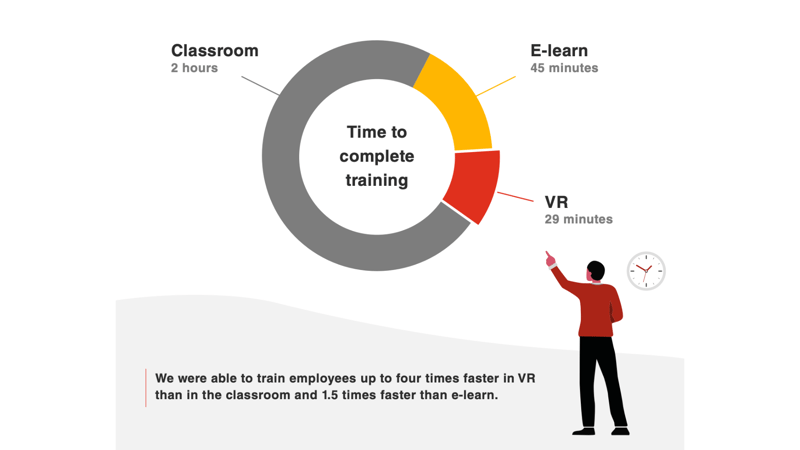
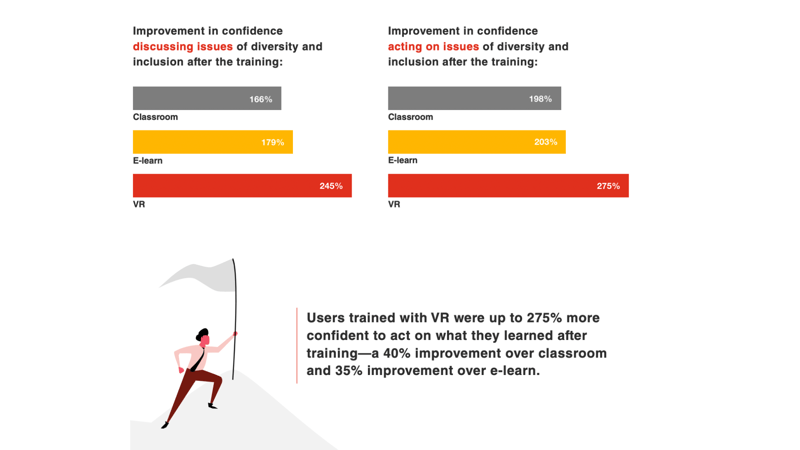
Employees trained using VR were more confident
Users trained with VR demonstrated up to a 275% increase in confidence in applying what they learned—an improvement of 40% over classroom training and 35% over e-learning. They were nearly 2.5 times more confident in discussing diversity and inclusion issues and almost three times more confident in acting on these issues following VR training. This is particularly noteworthy because confidence is a crucial factor for success in soft skills development. Enhanced self-belief not only helps learners connect more effectively with others but also leads to greater satisfaction with the training experience.
Employees trained using VR had a stronger emotional connection to the content
V-learners felt 3.75 times more emotionally connected to the content compared to classroom learners and 2.3 times more connected than e-learners. Emotional engagement plays a crucial role in deepening understanding and retention. For instance, viewing a compelling photo of a wildfire can create a stronger emotional impact than simply reading a fact-filled analysis about climate change and wildfires. This underscores how VR headsets can enhance emotional connections during training, leading to more impactful and memorable learning experiences. In the context of VR for business and industries like oil and gas, this emotional depth can drive more effective training and improved outcomes.
.png?width=800&height=450&name=Average%20emotional%20connection%20(1).png)
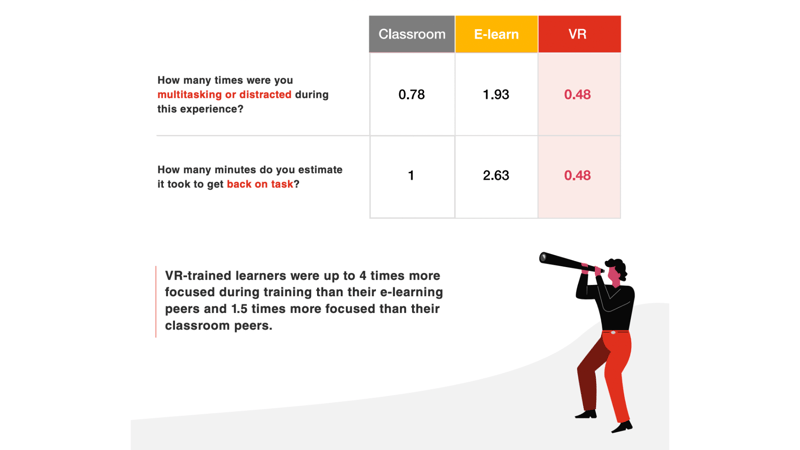
Employees trained using VR were more focused
Considering how VR operates, it's clear why users might experience fewer distractions with this technology: the simulations and immersive environment capture their full visual and cognitive attention. In our study, learners trained with VR were up to four times more focused during training compared to their e-learning counterparts and 1.5 times more focused than those in classroom settings. Immersion in a VR experience tends to enhance engagement, leading to a more effective learning process and potentially better training outcomes.
VR can be more cost-effective at scale
When PwC decided to evaluate the effectiveness of VR training, we also compared the costs of developing each learning modality. To do this, we designed and built a course that could be replicated across classroom, e-learning, and VR formats. We found that while VR requires a higher initial investment for development and deployment compared to classroom or e-learning training, it can be more cost-effective at scale.
Our analysis revealed that developing a custom VR course was 47% more expensive than a classroom course and 48% more than an e-learning course. This higher cost reflects not only the creation of the content but also the need for specialised resources such as 3D artists and software developers, which are not required for traditional classroom or e-learning content. However, considering the return on investment (ROI), VR training becomes more advantageous. VR training is completed faster than both classroom and e-learning courses, which reduces the overall cost when factoring in employees' time. Thus, VR can offer a better return on investment, especially when accounting for the time saved. The graph below illustrates PwC’s total cost savings and the point at which we achieved a break-even on training our learner population.
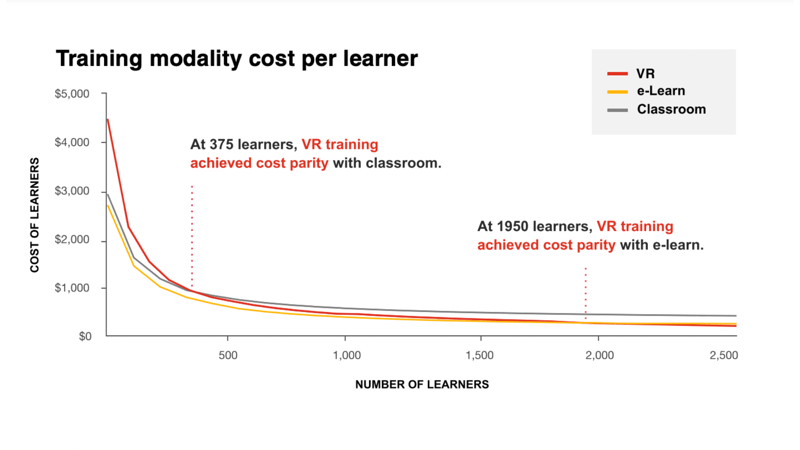
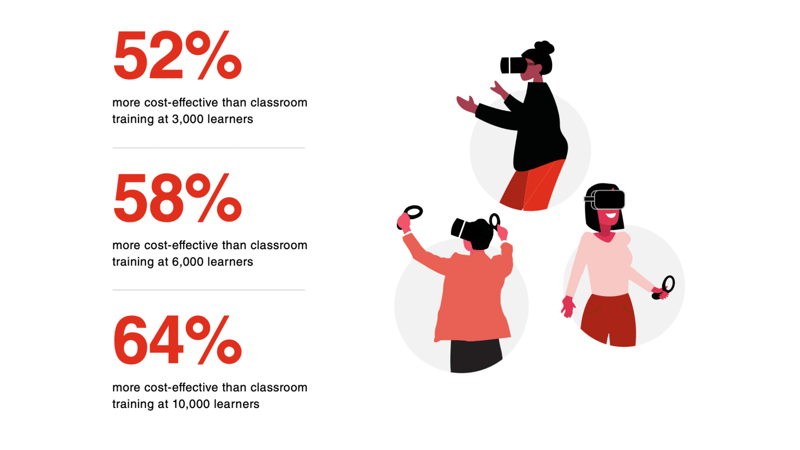
Even with onboarding times included, we estimated that VR training costs would equal those of classroom training with just 375 learners. As the number of learners increases, the cost advantages of VR become even more pronounced. For instance, with 3,000 learners, VR costs are 52% less than classroom training; with 6,000 learners, they drop to 58% less; and with 10,000 learners, VR costs are 64% less. Since employee time is valuable, reducing training time leads to faster achievement of a positive ROI.
When comparing VR training ROI to e-learning, a higher number of learners is required to reach cost parity due to e-learning's lack of facilitator/trainer costs. We found that VR costs would equal those of e-learning with 1,950 learners. As the number of learners grows, the cost benefits of VR become evident: at 3,000 learners, VR costs are 8% less; at 6,000 learners, 20% less; and at 10,000 learners, 26% less. As with classroom training, quicker employee return to work results in a faster attainment of positive ROI.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this study of VR training at PwC highlights its significant potential as a transformative tool in employee development. VR training not only enhances engagement and emotional connection, but it also accelerates learning and boosts confidence in applying new skills. Despite the higher initial investment required for VR course development, the long-term cost advantages become clear when scaled to larger learner populations. Specifically, VR training can be up to 64% less expensive than traditional classroom training and offers substantial cost savings compared to e-learning as well.
The immersive nature of VR headsets ensures that learners remain highly focused, resulting in faster completion times and greater effectiveness. As we observed, VR training delivers impressive ROI by reducing overall training time and associated costs. Furthermore, the emotional impact and deeper connection with the content foster better learning outcomes and enhanced skill application.
Given these findings, VR training emerges as a powerful option for businesses, particularly in sectors like oil and gas, where immersive experiences can significantly impact safety and operational efficiency. Integrating VR into a blended learning approach can provide an industry-leading training solution that combines the strengths of traditional methods with the innovative benefits of virtual reality. As we move forward, VR's role in enterprise training is poised to grow, driving a new era of cost-effective, immersive, and impactful learning.
How would we use these findings?
Imagine a set of VR Mixed reality Meta 3 Quest headsets and the impact on your training content:-
- Faster Absorption
- Faster learning at a lower cost (£479 per headset)
- Then add 3D learning with Microsoft Mesh rooms, with a Teams premium license
- Your Training, Induction or Milk round would be transformed
If you'd like to know more we can help.

